Once the rainy season arrives, the locals in the mushroom-producing areas like to carry bamboo baskets on their backs and search for and pick wild mushrooms all over the mountains and fields. China has a vast land area and a relatively large forest area. Moreover, most of China’s territory is located in the temperate and tropical climate zones, so a large number of fungi grow.
At present, many edible wild mushrooms have not been artificially cultivated on a large scale. However, due to their delicious taste and high nutritional value, they are loved and sought after by people. How many of the following famous wild mushrooms have you seen?
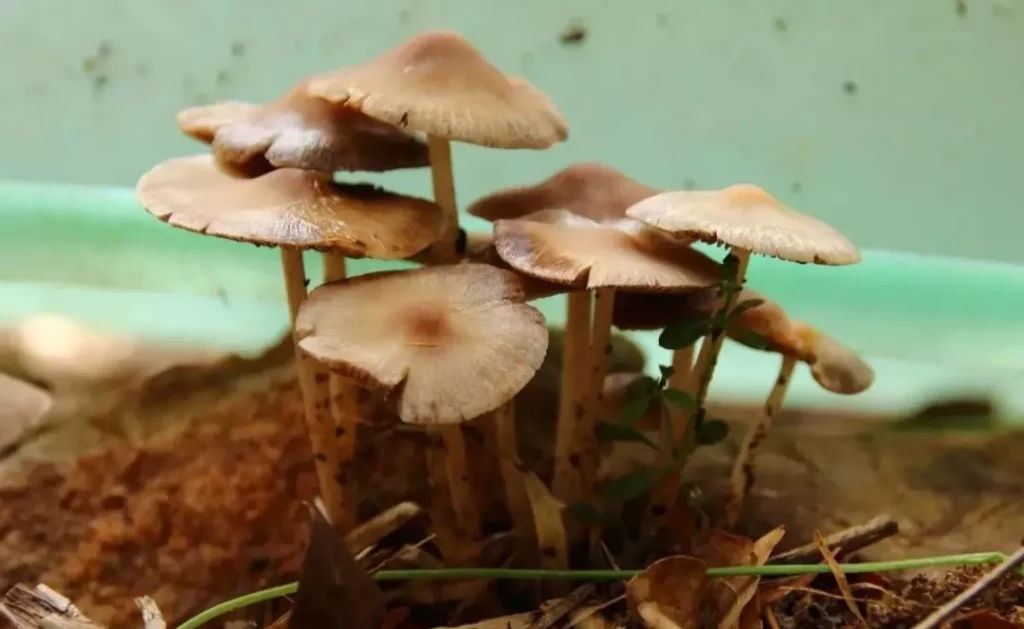

Termite Mushroom (Termitomyces albuminosus)
Termite mushroom is a precious and famous edible fungus that is a specialty of Yunnan Province. It is renowned for its tender and delicious texture, and it contains various nutrients such as calcium, phosphorus, iron, and protein, and has an especially sweet and fresh taste. There are many varieties of termite mushrooms, including the black-skinned termite mushroom, green-skinned termite mushroom, white-skinned termite mushroom, and grass-skinned termite mushroom, etc. Among them, the black-skinned termite mushroom is of better quality.
The harvesting season of termite mushrooms is from June to September every year. They mostly grow on the slopes of unpolluted red soil mountain forests or beside the nests of termites in the fields. When the mushroom cap emerges from the ground, it looks like a garlic bulb, and then it gradually spreads out like an umbrella. The mushroom stem is solid, with a smooth surface, and the flesh is tender and easy to break. There are many ways to cook termite mushrooms, and they are suitable for stir-frying, cooking, and making soup. Various famous dishes can be made with termite mushrooms, such as cold dressed termite mushrooms, braised termite mushrooms in soy sauce, pan-fried termite mushrooms, and ham with termite mushrooms, etc.
Termite mushrooms can be made into dried termite mushrooms, pickled termite mushrooms, or termite mushrooms in oil through sun-drying, salting, or frying in vegetable oil. They can be stored for a long time for year-round consumption, and they still retain the special flavor of termite mushrooms when eaten.

Bamboo Pith
Bamboo pith, also known as Dictyophora indusiata, bamboo ginseng, and Monachus terin, is a precious and famous edible fungus that is a specialty of Yunnan Province. It mainly grows in the bamboo forests in Zhaotong Prefecture of Yunnan Province and in the southern part of Yunnan Province. Bamboo pith is a kind of cryptogamous fungus that parasitizes on the roots of bitter bamboo, and its shape is slightly similar to a gas lamp mantle.
It has a dark green mushroom cap, a snow-white cylindrical mushroom stem, a pink egg-shaped volva. At the top of the mushroom stem, there is a delicate and white net-like skirt that spreads downward from the mushroom cap. The whole mushroom body looks very beautiful and is known as the “flower of fungi” by people.
Bamboo pith is rich in nutrients such as protein, fat, and carbohydrates. The flesh of the fungus is white in color, tender in texture, and emits a pleasant fragrance. When cooking dishes with bamboo pith, the taste is delicious, crisp, and palatable. In summer, when cooking dishes or making soup, putting a little bamboo pith in it has the special function of preventing spoilage and prolonging the storage time.

Matsutake Mushroom
Matsutake mushroom is a precious wild fungus. Its scientific name is Tricholoma matsutake, and it is also known as big flower fungus, pine fungus, and peeling fungus. It is a precious edible fungus and enjoys the reputation of the “King of Mushrooms” in Japan. Matsutake belongs to the Basidiomycetes class and grows in pine forests and mixed coniferous and broad-leaved forests. Mushrooms emerge from July to September every year.
Yunnan Province has many mountains and dense forests, which are suitable for the growth of matsutake mushrooms. Matsutake mushrooms are abundantly produced in northwestern and central Yunnan. Fresh matsutake mushrooms are umbrella-shaped, with a distinct color. The mushroom cap is brown, and the mushroom stem is white. Both have fibrous villous scales. The flesh of the mushroom is thick, tender, and white, with a strong and unique aroma.
Matsutake mushrooms are rich in nutrients, containing protein, amino acids, various vitamins, carbohydrates, and minerals. In addition, matsutake mushrooms are rich in mushroom polysaccharides and have anti-cancer effects. There are various ways to cook matsutake mushrooms, and they are suitable for roasting, stir-frying, and boiling. When eaten, they are sweet and delicious, with a strong aroma. After eating, the lingering fragrance remains in the mouth, making it thought-provoking.
The matsutake mushrooms growing in Yunnan are large in size, with thick stems. The flesh is purely white, tender, and has a strong fragrance. Matsutake mushrooms have high nutritional value, a delicious taste, and high medicinal value. In ancient times, both in Europe and Japan, matsutake mushrooms were regarded as delicacies from the mountains. In Japan, they are high-grade gifts and were used as tributes presented by the common people to the nobility and the royal family in ancient times.

Boletus Mushroom
Boletus mushroom is a general term for fungi of the family Boletaceae, the family Strobilomycetaceae, etc. Yunnan Province is rich in boletus mushroom resources. The edible boletus mushrooms mainly include white, yellow, and black boletus mushrooms. The white boletus mushroom is also known as the porcini mushroom.
It grows in the mixed pine and oak forests at an altitude between 900 meters and 2,200 meters, or at the edge of the forest that has been cut down not long ago. The growing period is from the end of May to the middle of October every year. There are more of them growing after the rain when the sky clears. The white boletus mushroom tastes delicious and is rich in nutrients. Not only in Yunnan Province, but also in Western European countries, there is a widespread habit of eating white boletus mushrooms.
In addition to being eaten fresh, boletus mushrooms can also be dried and sliced to be processed into dry goods that can be stored for a long time. The yellow and black boletus mushrooms belong to the same family as the white boletus mushroom, and they have the same way of cooking and a similar taste.
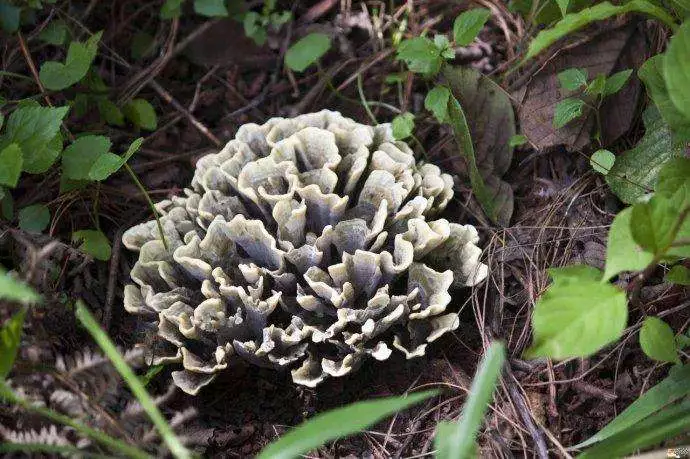

Thelephora ganbajun
Thelephora ganbajun is a rare and precious wild edible fungus unique to Yunnan Province. Its scientific names include Sparassis crispa, Hydnum repandum, etc. It grows among the pine trees in the mountain forests of central and western Yunnan. It tastes extremely delicious and is a top-grade wild edible fungus.
It grows under the masson pine trees from July to September every year. This kind of fungus has no mushroom caps or gills. It grows in clusters and looks like the teeth of cows or horses, so people vividly call it the “cow tooth fungus”.
When Thelephora ganbajun first emerges from the ground, it is yellowish-brown in color, and when it is fully mature, it turns dark brown. The flesh of Thelephora ganbajun is tough and is rich in nutrients such as calcium, iron, thiamine, and protein. Thelephora ganbajun has a strong fragrance that is very similar to that of dried salted beef. In Yunnan, dried salted beef is called “ganba”, so this fungus is named Thelephora ganbajun.
Thelephora ganbajun is suitable for stir-frying, and it can be cooked with either meat or vegetables. When stir-frying it without meat, tear the Thelephora ganbajun into thin shreds, wash them, and then add shredded green peppers, garlic, salt, etc., and stir-fry until cooked. The price when it is freshly on the market is about 100 yuan per kilogram. Canned Thelephora ganbajun is available for sale in various grocery stores and shopping malls.

Sarcodon imbricatus
Sarcodon imbricatus grows deep in the grass on the cliffs of high mountains from August to September every year. It is produced in Chuxiong Yi Autonomous Prefecture and Lijiang Naxi Autonomous County. This kind of fungus has neither a cap nor a stem. It is covered with a layer of fine villi, which is yellowish-brown in color and has obvious black patterns. It looks like the claws of a tiger, so it gets its name.
Sarcodon imbricatus has high nutritional and economic values. Fresh Sarcodon imbricatus has a strong fragrance, and the fragrance becomes even stronger after it is dried. “Unusual shape and wonderful aroma” are the two major characteristics of Sarcodon imbricatus.
Cut the washed Sarcodon imbricatus into thick shreds. Put them into the pot together with mung bean sprouts and shredded pork tenderloin, add seasonings and stir-fry. Then pour on the cooked chicken oil, and the dish “Stir-fried Sarcodon imbricatus with Shredded Pork and Mung Bean Sprouts” is ready. This dish has an aromatic smell and a special taste, and it is a top-grade dish among edible fungus dishes.

Tremella aurantia
Tremella aurantia is also known as yellow tremella because of its golden color, and it is also called brain tremella because it resembles a human brain. Tremella aurantia is a rare and precious edible fungus produced in Yunnan Province. It is mainly produced in the river valley areas within the Jinsha River Basin, such as Lijiang, Weixi, Shangri-La, and Deqin.
Tremella aurantia is rich in fat, protein, and trace elements such as phosphorus, sulfur, manganese, iron, magnesium, calcium, and potassium. It is a nutritious tonic and can also be used medicinally.
According to “Chinese Medicinal Fungi”, Tremella aurantia is warm in nature with a slight cold property, sweet in taste. It can resolve phlegm, relieve cough, relieve asthma, regulate qi, soothe the liver and intestines. It mainly treats symptoms such as lung heat, excessive phlegm, common cold and cough, asthma, and hypertension.
Tremella aurantia is mainly used to make various vegetarian dishes. The vegetarian dishes cooked with Tremella aurantia have a special color, aroma, and taste, and they are rare delicacies on the banquet table. Tremella aurantia is rich in gum. When stewed with rock sugar, it is not only smooth and tender, but also has the health care effect of clearing the mind and nourishing the brain.
Tremella aurantia requires suitable natural conditions for growth, and its output is limited, making it extremely precious. Yunnan Province has been exporting Tremella aurantia for many years, mainly to Southeast Asia, and there is a shortage of supply to meet the demand.
- 2025: The Year Agriculture Enters the AI Era – A New Wave of Transformation on the Horizon IAgricultural AI Revolution
- Algarikon Zero Project: How a Spanish Firm Transforms Invasive Algae for Edible Mushroom Cultivation
- 🔍 Research Uncovers Key Mechanisms of Morel Strain Degradation
- Spain: Edible Mushrooms Found to Alleviate the “Salty” Dilemma of the Meat Industry
- Yunnan’s Morel Mushroom Industry: Current Status and Prospects